Integrating Sigrid CI with Azure DevOps
This documentation covers cloud-based Sigrid. For on-premise Sigrid, refer to the section about on-premise analysis configuration.
Prerequisites
- You have a Sigrid user account.
- You have created an authentication token for using Sigrid CI.
- Python 3.7 or higher needs to be available in the CI environment if you do not use the Docker image published by SIG. The client scripts for Sigrid CI are based on Python.
- The examples assume Git is available on your Azure DevOps environment.
- Sigrid CI requires the UTF-8 character encoding, as we use emoji in the command line output. Nowadays UTF-8 is the default in most environments, but if you are using a different character encoding for Python you will need to set the character encoding explicitly using the PYTHONIOENCODING environment variable (i.e.
export PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8orset PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8).
On-boarding your system to Sigrid
On-boarding is done automatically when you first run Sigrid CI. As long as you have a valid token, you will receive the message system has been on-boarded to Sigrid. Subsequent runs will then be visible in both your CI environment and sigrid-says.com.
Configuration
Step 1: Enable pull request comment feedback
Sigrid CI can provide feedback as pull request comments. This makes easier to process Sigrid’s feedback during your pull request review, as the feedback is more visual and it also reduces the number of clicks you need to read the feedback.
- Azure DevOps will, by default, not run pipelines for pull requests. You need to enable this manually via “build policies” in your organization or project settings. You can find more information on this in the Azure DevOps documentation. Note that automatically running pipelines for pull requests is a general best practice, so enabling this setting has benefits beyond Sigrid.
- To create a pull request comment, the
<repo name> Build Serviceuser must have theContribute to pull requestspermission. You can find information on how to edit user permissions in the Azure DevOps documentation.
Step 2: Create pipeline configuration file
We will create a pipeline that consists of two jobs:
- One job that will publish the main/master branch to sigrid-says.com after every commit.
- One job to provide feedback on pull requests, which can be used as input for code reviews.
Alternative 2a: Docker-based analysis
The recommended approach is to run Sigrid CI using the Docker image published by SIG. Please make sure you use the azure tag. In the root of your repository, create a file azure-devops-pipeline.yaml and add the following contents:
stages:
- stage: Report
jobs:
- job: SigridCI
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
container: softwareimprovementgroup/sigridci:azure
continueOnError: true
condition: "ne(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main')"
steps:
- checkout: self
fetchDepth: 0
clean: true
- bash: "sigridci.py --customer <example_customer_name> --system <example_system_name> --source .
env:
SIGRID_CI_TOKEN: $(SIGRID_CI_TOKEN)
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
PYTHONIOENCODING: utf8
PYTHONUTF8: "1"
continueOnError: true
- job: SigridPublish
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
container: softwareimprovementgroup/sigridci:azure
continueOnError: true
condition: "eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main')"
steps:
- checkout: self
fetchDepth: 0
clean: true
- bash: "sigridci.py --customer <example_customer_name> --system <example_system_name> --source . --publishonly"
env:
SIGRID_CI_TOKEN: $(SIGRID_CI_TOKEN)
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
PYTHONIOENCODING: utf8
PYTHONUTF8: "1"
continueOnError: true
Note the name of the branch, which is main in the example but might be different for your repository. In general, most older projects will use master as their main branch, while more recent projects will use main.
Commit and push this file to the repository, so that Azure DevOps can use this configuration file for your pipeline. If you already have an existing pipeline configuration, simply add these steps to it.
Security note: The softwareimprovementgroup/sigridci:azure Docker image deliberately runs as root (in other words, we deliberately did not include a USER instruction in the Dockerfile that generates this image). Based on Microsoft’s documentation, we understand that Linux-based Docker images used in Azure DevOps need to run as root (fifth requirement).
Alternative 2b: Download Sigrid CI client script
If you are unable to use Docker, for example because you are using local runners, you can still use Sigrid CI by downloading the Sigrid CI client script directly from GitHub. In the root of your repository, create a file azure-devops-pipeline.yaml and add the following contents:
stages:
- stage: Report
jobs:
- job: SigridCI
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest' #https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/pipelines/agents/hosted?view=azure-devops&tabs=yaml#software
continueOnError: true
condition: "ne(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main')"
steps:
- checkout: self
fetchDepth: 0
clean: true
- bash: "git clone https://github.com/Software-Improvement-Group/sigridci.git sigridci"
displayName: Clone SigridCI from Github
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
displayName: Get PythonTools
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.9'
addToPath: false
- bash: "./sigridci/sigridci/sigridci.py --customer <example_customer_name> --system <example_system_name> --source ."
env:
SIGRID_CI_TOKEN: $(SIGRID_CI_TOKEN)
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
PYTHONIOENCODING: utf8
PYTHONUTF8: "1"
continueOnError: true
- job: SigridPublish
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
continueOnError: true
condition: "eq(variables['Build.SourceBranch'], 'refs/heads/main')"
steps:
- checkout: self
fetchDepth: 0
clean: true
- bash: "git clone https://github.com/Software-Improvement-Group/sigridci.git sigridci"
displayName: Clone SigridCI from Github
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
displayName: Get PythonTools
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.9'
addToPath: false
- bash: "./sigridci/sigridci/sigridci.py --customer <example_customer_name> --system <example_system_name> --source . --publishonly"
env:
SIGRID_CI_TOKEN: $(SIGRID_CI_TOKEN)
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
PYTHONIOENCODING: utf8
PYTHONUTF8: "1"
continueOnError: true
Note the name of the branch, which is main in the example but might be different for your repository. In general, most older projects will use master as their main branch, while more recent projects will use main.
Security note: This example downloads the Sigrid CI client scripts directly from GitHub. That might be acceptable for some projects, and is in fact increasingly common. However, some projects might not allow this as part of their security policy. In those cases, you can simply download the sigridci directory in this repository, and make it available to your runners (either by placing the scripts in a known location, or packaging them into a Docker container).
Commit and push this file to the repository, so that Azure DevOps can use this configuration file for your pipeline. If you already have an existing pipeline configuration, simply add these steps to it.
Step 3: Analysis configuration
In both alternatives, the relevant command that starts Sigrid CI is the call to the sigridci.py script, which starts the Sigrid CI analysis. The scripts supports a number of arguments that you can use to configure your Sigrid CI run. The scripts and its command line interface are explained in using the Sigrid CI client script.
Sigrid will try to automatically detect the technologies you use, the component structure, and files/directories that should be excluded from the analysis. You can override the default configuration by creating a file called sigrid.yaml and adding it to the root of your repository. You can read more about the various options for custom configuration in the configuration file documentation.
Step 4: Create your Azure DevOps pipeline
In Azure DevOps, access the section “Pipelines” from the main menu. In this example we assume you are using a YAML file to configure your pipeline:

Select the YAML file you created in the previous step:
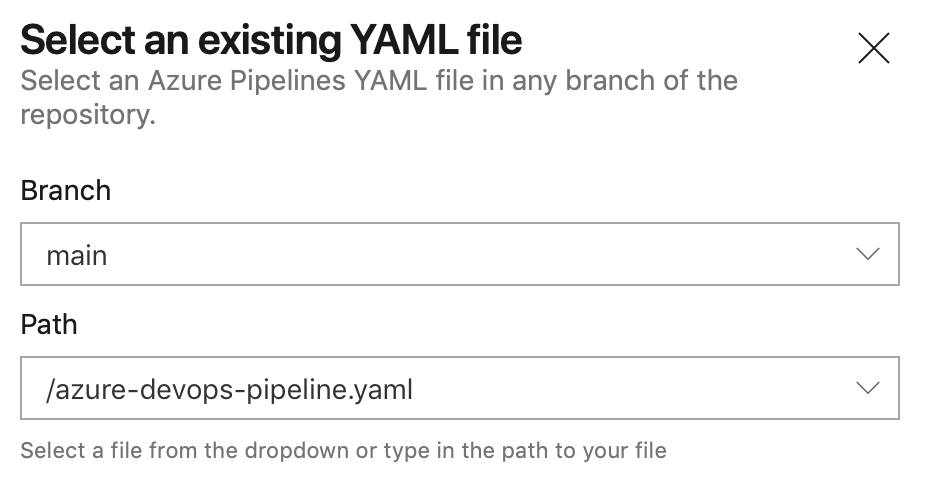
This will display the contents of the YAML file in the next screen. The final step is to add your account credentials to the pipeline. Click “Variables” in the top right corner. Create a secret named SIGRID_CI_TOKEN and use your Sigrid authentication token as the value.

From this point, Sigrid CI will run as part of the pipeline. When the pipeline is triggered depends on the configuration: by default it will run after every commit, but you can also trigger it periodically or run it manually.
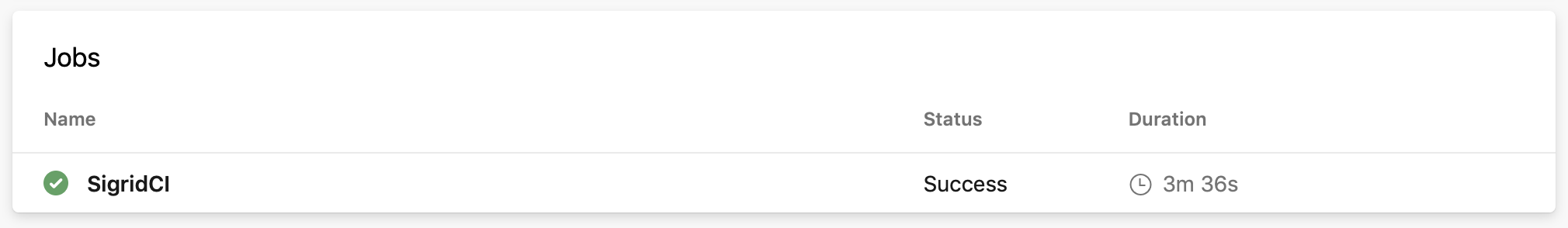
Usage
To obtain feedback on your commit, click on the “Sigrid CI” step in the pipeline results screen shown above.

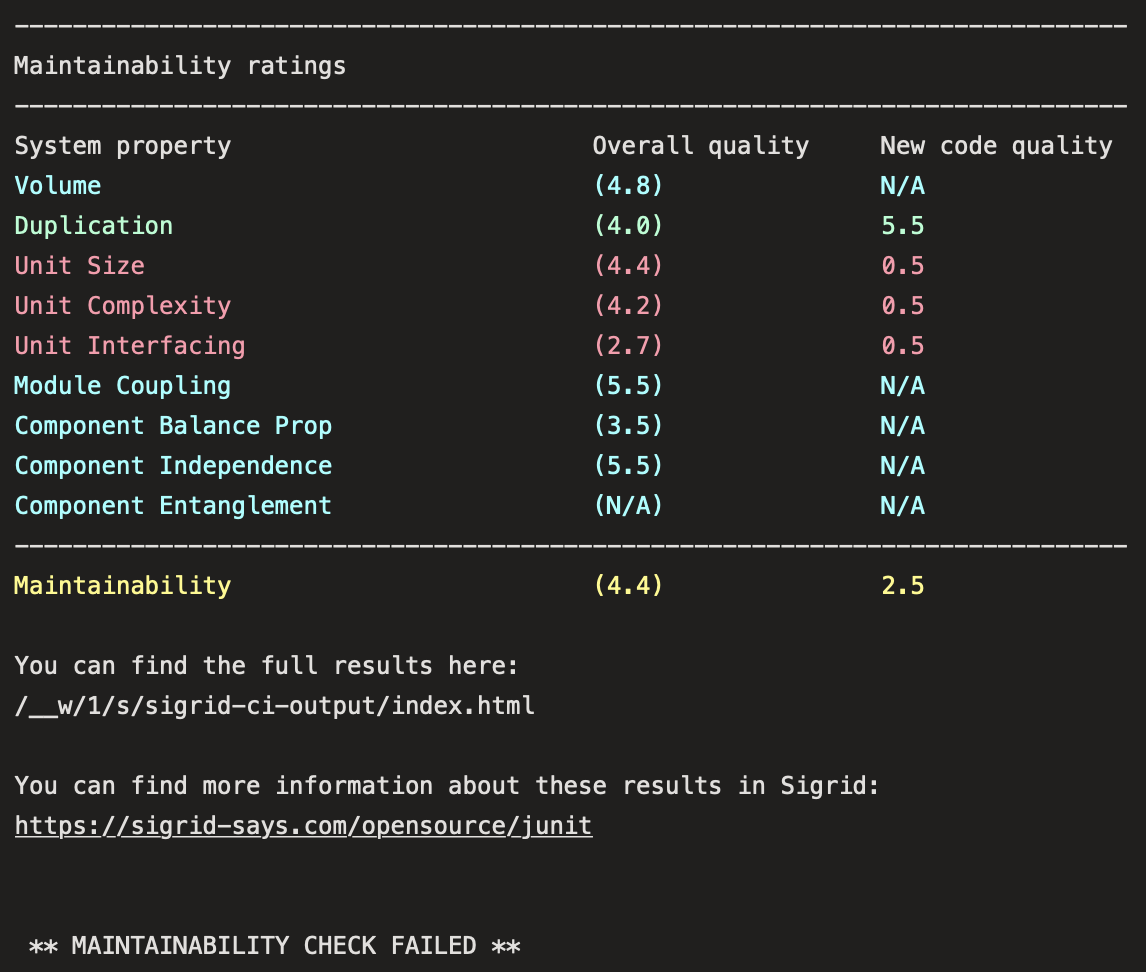
The check will succeed if the code quality meets the specified target, and will fail otherwise. In addition to the simple success/failure indicator, Sigrid CI provides feedback as comments in your pull request:
Contact and support
Feel free to contact SIG’s support team for any questions or issues you may have after reading this documentation or when using Sigrid.

